Water meters are an integral part of Hong Kong’s water supply system and have been in use since the late 19th century. Because clean water is such a valuable resource, meters are installed in every Hong Kong household to record a consumer’s water consumption. Over time, water meter models have changed and evolved. For example, water meters were replaced in the 1970s following the adoption of the metrication policy that changed the measurement of volume from imperial gallons to cubic metres. The campaign to promote the adoption of metrication at the time has signified Hong Kong’s move towards internationalisation. In recent years, water meters have become increasingly intelligent and these models are gradually being installed in new urban development areas. This initiative is another step towards the automation of all data recording.
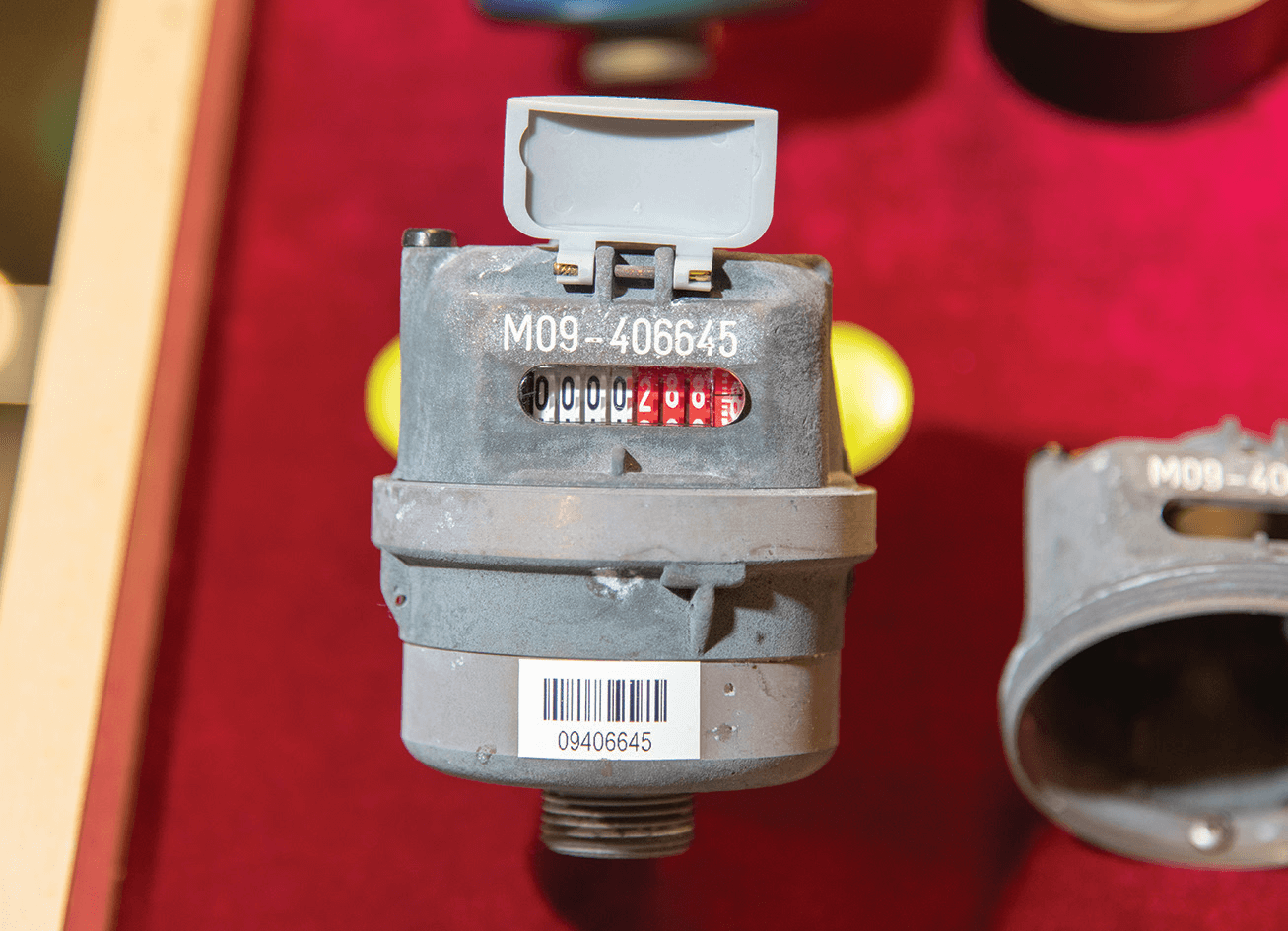
Water meters are installed in both commercial and residential units and individual consumers are allocated their own. Domestic water meters are typically 15 mm in diameter to cater for a small flow rate, while commercial water meters vary in size depending on the needs of the customer's industry and the size of the business. For instance, a “cha chaan teng” (restaurant serving local fast food) usually requires a 25 mm diameter water meter, whereas a Chinese restaurant with a high water flow may require a 100 mm diameter meter. For large-scale operations, such as amusement parks, the diameter of the meter can be as large as 200 mm. The WSD determines the required meter size based on demand during review of supply application.
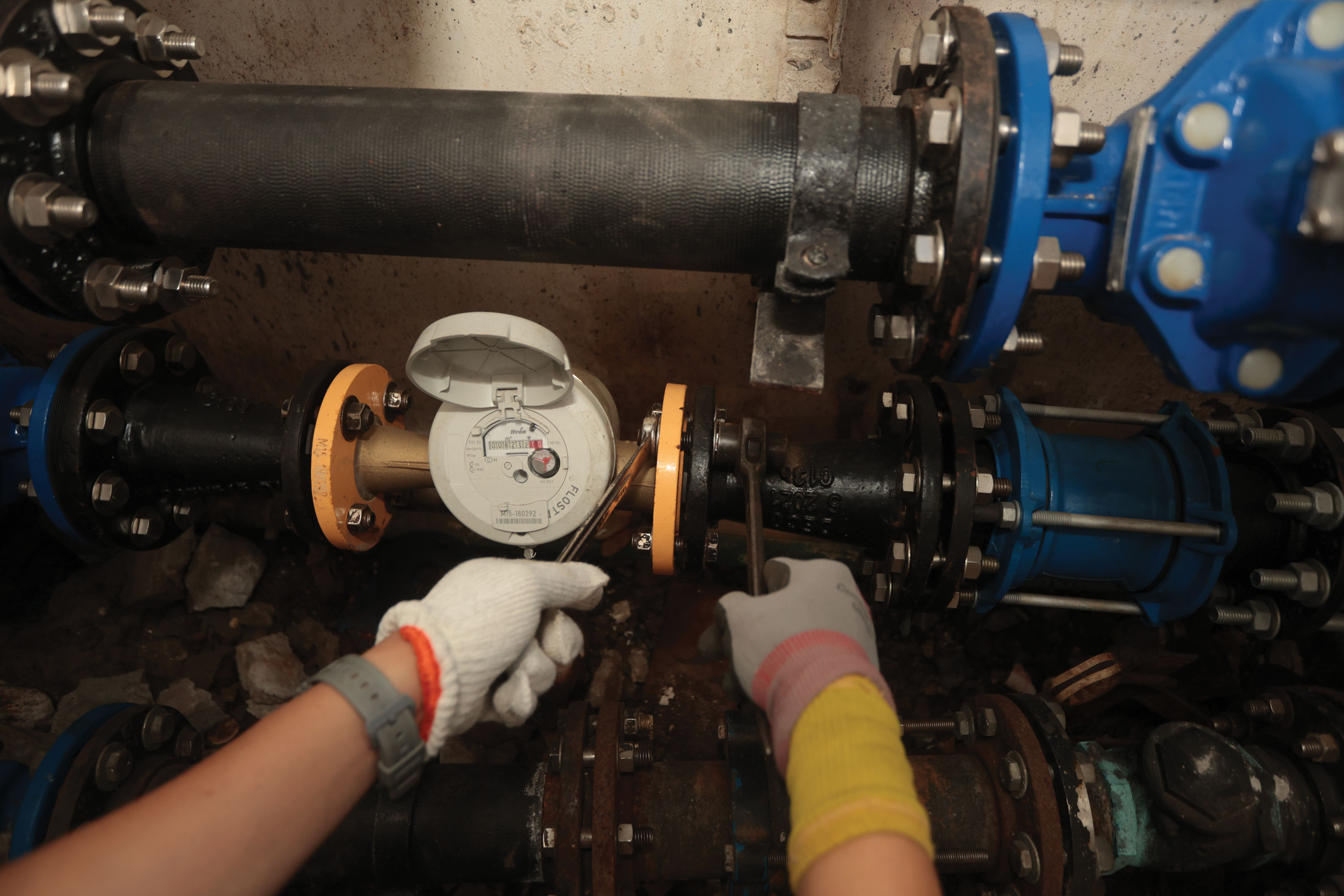

A Hong Kong urban myth from the past says the elderly used to collect water from a trickling hosepipe, and due to its weak water-flow the meter’s water counter would not correctly operate, resulting in a lower water bill. The myth is actually true, as water meters need a certain strong flow of water to drive the inside gears to measure the water volume flow. However, with the adoption of advanced technology, water meters now accurately measure the flow and there is no longer any “free water”.

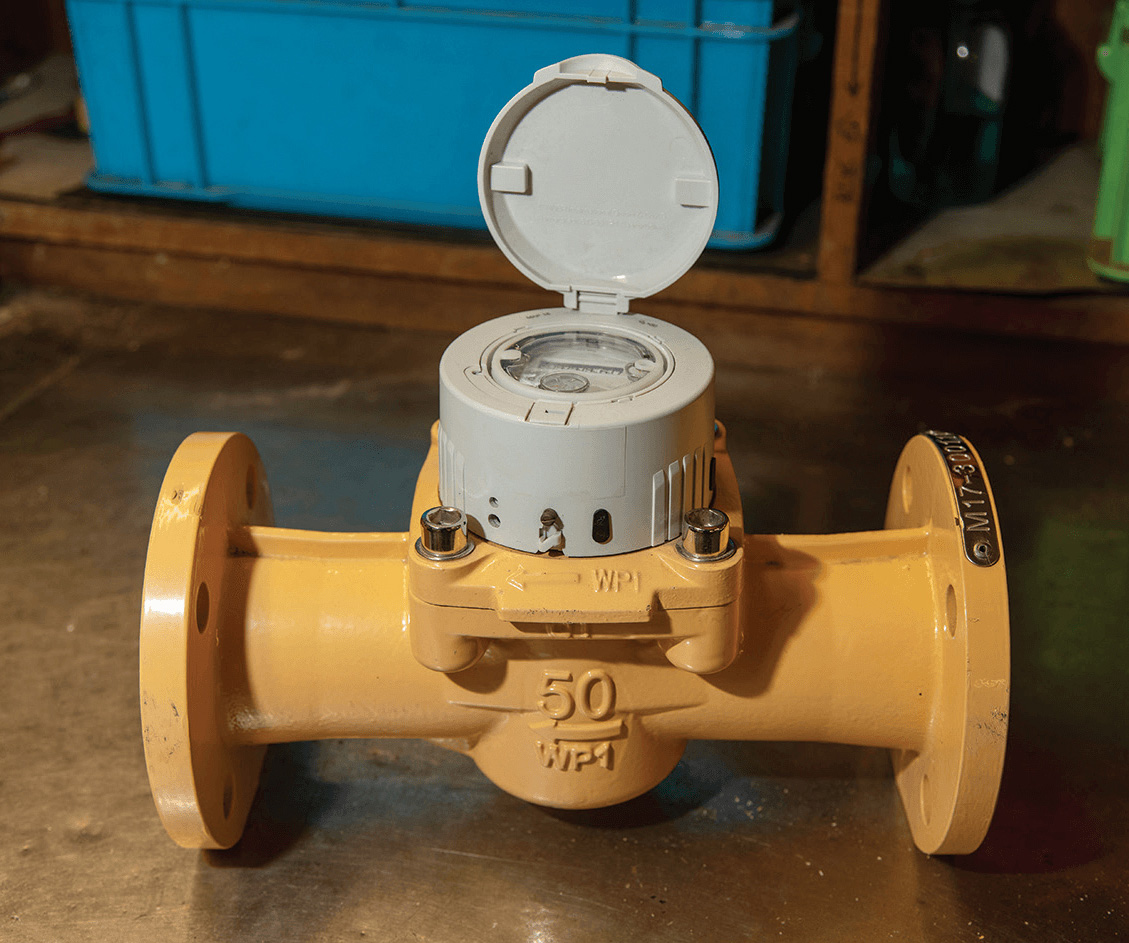
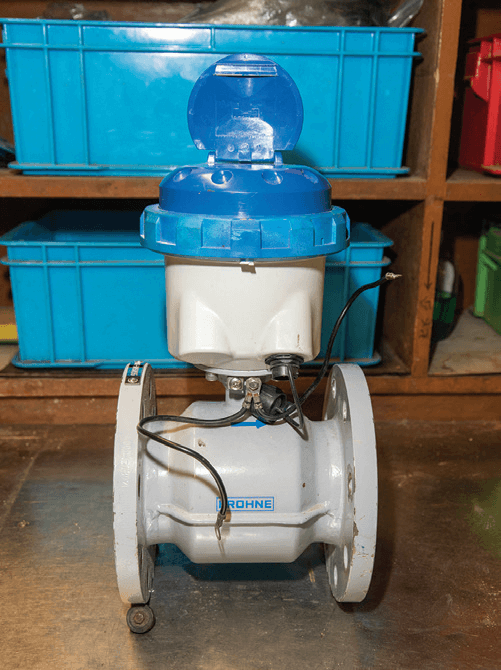
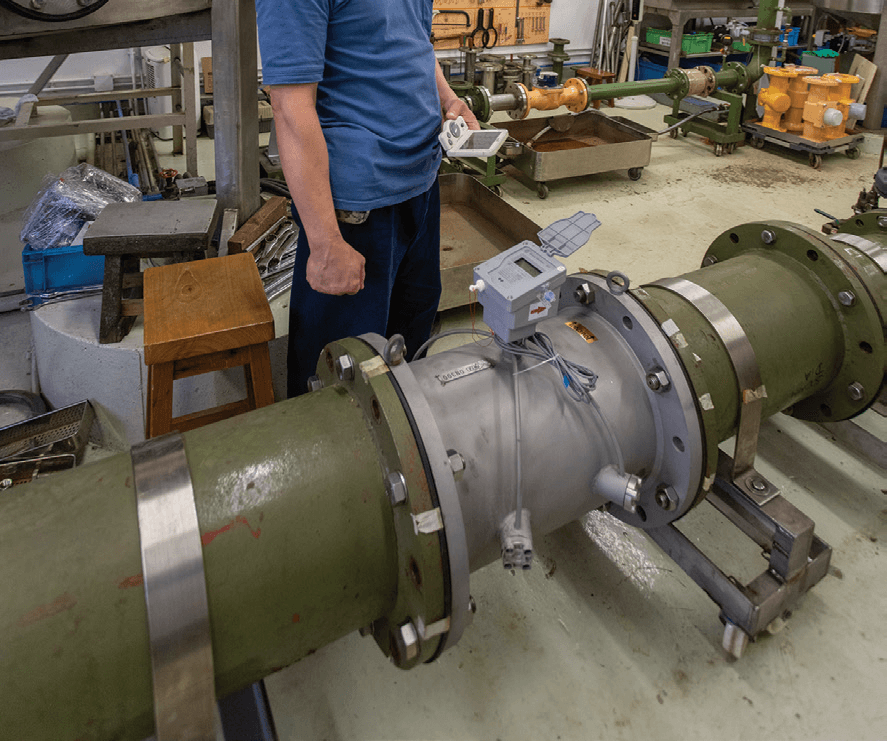
The WSD has recently introduced the Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI - formerly named the Automatic Meter Reading (AMR)) system, which combines the functions of a new generation of smart meters, AMI Outstation and AMI Master Station. The AMI system provides the Water Authority (WA) with timely and historical metering data, status information and alert signals for the operation and monitoring of smart water meters. Consumers in buildings with smart meters can download the AMI mobile application to access on-demand water consumption data and an estimate of water charges at their convenience. Information from the AMI system assists in long-term water resource management and water conservation.
The government now includes the AMI system in the land sale conditions of suitable new sites and into the design of new buildings to be built on those sites. As of August 2022, the WSD has received over 100 applications for AMI systems, involving over 250 new buildings and around 70,000 smart water meters. This will assist Hong Kong in progressing towards a greener and smarter community.
The New Generation Smart Water Meter System: Advanced Metering Infrastructure System Accessories and Equipment




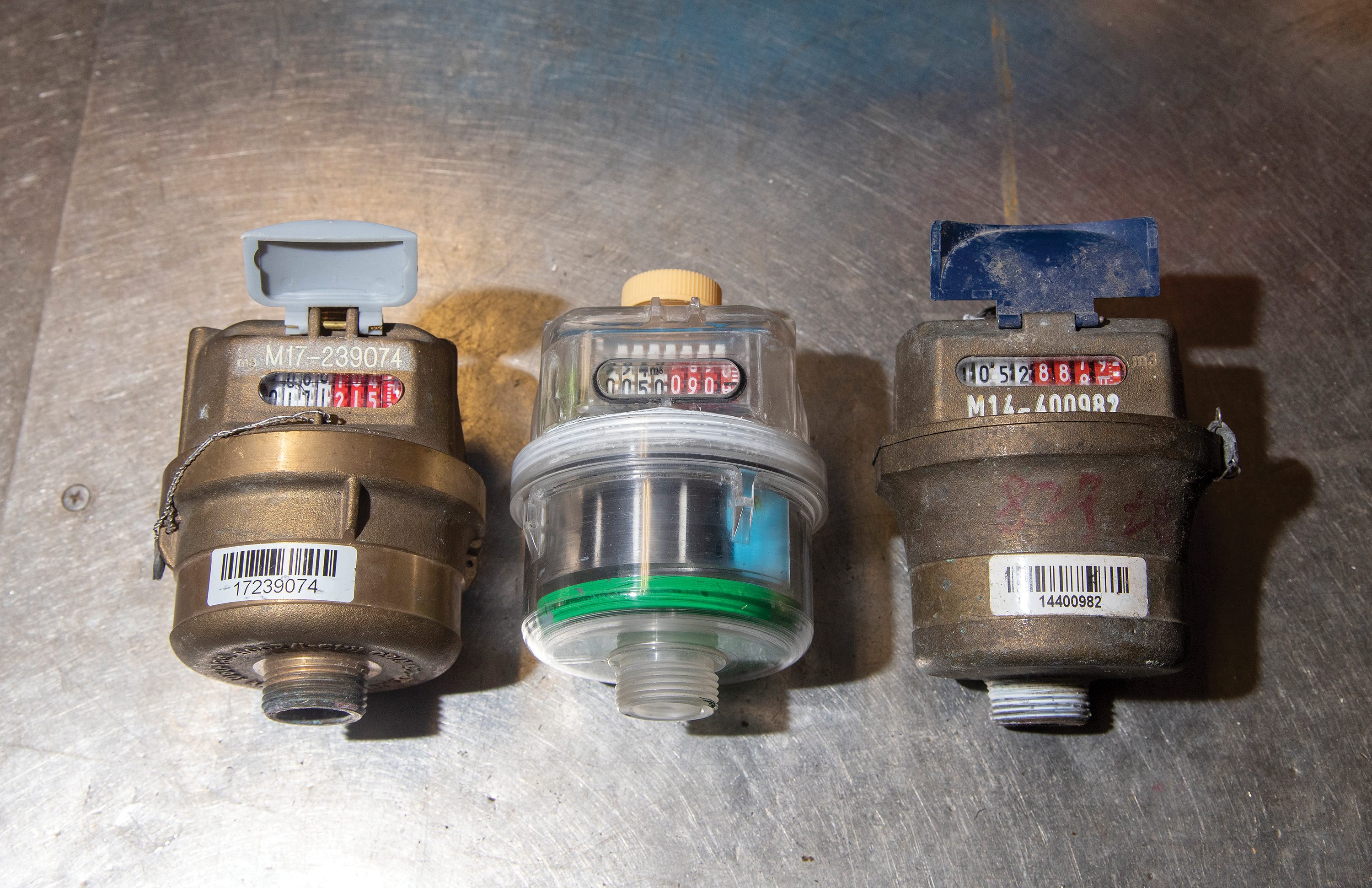
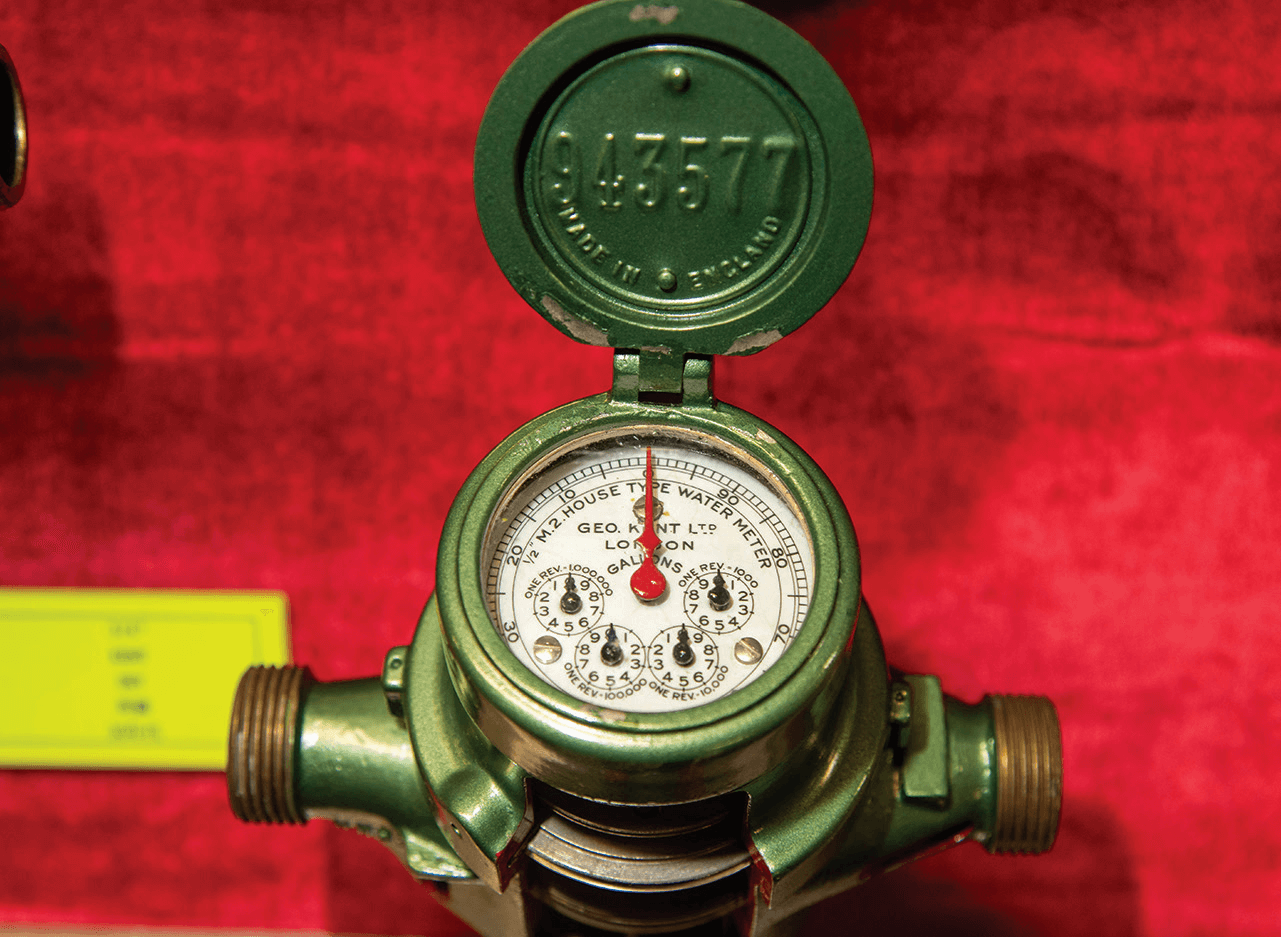
This is one of the earliest water meters preserved by the WSD and has an exclusive emerald colour. It uses water flow to drive the gears and a pointer to indicate the amount of water used. The meter reading is in gallons and has a protective cover.
The 1960s rotary piston water meter is coloured blue, representing water. The water meter is fitted with a filter at the water inlet to stop debris, and the flow measurement has been changed from a velocity to a volumetric measurement for better accuracy.
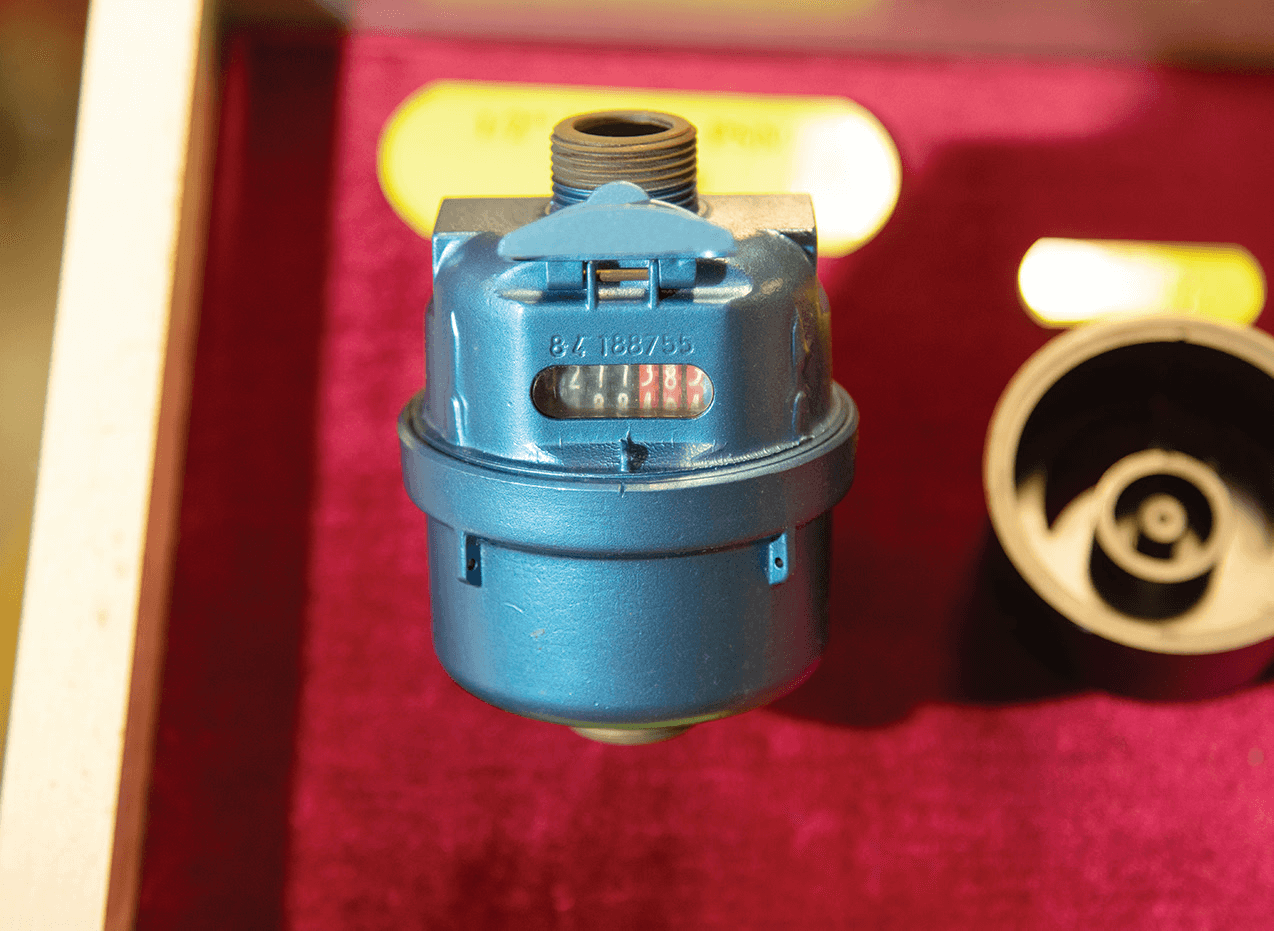
After the 1970s the unit of measurement was changed from the imperial gallon to the decimal cubic metre, in keeping with Hong Kong’s change to decimal units of measurement. It signified entry into a new era of globalisation.